A linked list is an important programming concept that underlies a lot of modern data structures. Linked List is a linear data structure, in which elements are not stored at a contiguous location, rather they are linked using pointers. Linked List forms a series of connected nodes, where each node stores the data and the address of the next node.
Types of linked list:
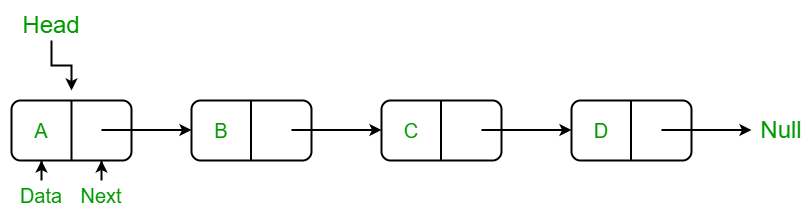
1. Singly linked list:
In a singly linked list, each node contains a reference to the next node in the sequence. We can only traverse the single linked list in one direction.
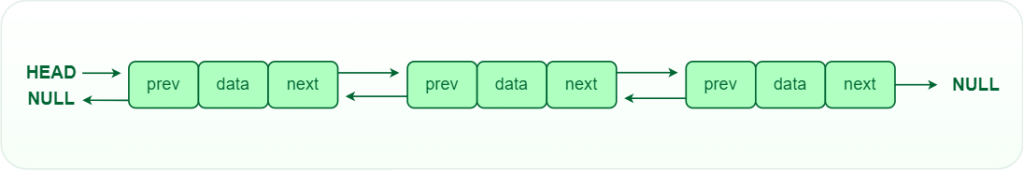
2. Doubly linked list:
In a doubly linked list, each node contains references to both the next and previous nodes. Because of the next and previous references, we can traverse the doubly linked list in both directions. On the other hand, these references require more memory space comparing with singly linked list.
3. Circular linked list:
In a circular linked list, the last node points back to the head node, creating a circular structure. It can be either singly or doubly linked.

Advantage of linked list:
- Dynamic Size: A single node can be inserted or deleted from the linked list during the runtime. But we need to be careful when durling with the reference of next or prev.
- Insertion and Deletion: Inserting or deleting a node from a linked list is efficient, we only need to modify the reference rather than shifting the whole list.
- Flexibility: Linked lists can be easily reorganized and modified without requiring a contiguous block of memory.
Disadvantage of linked list:
- Random Access: We can’t use the index to access the specific node like list. Instead, traversal is required for searching.
- Extra Memory: Linked lists require additional memory for storing the references, compared to lists.
Here we will implement the simplifying singly linked list, more details will be shown in data structure.
# a class for a single node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# a class for a linked list
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# insert a node to the end
def insert(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
# if there is no node in the list
if self.head is None:
# the new node is the head of the list
self.head = new_node
# if there is some nodes in the list
else:
# find the last node
cur = self.head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
# add the new node to the end
cur.next = new_node
# delete a node from the end
def delete(self):
# if there is no node in the list, do nothing
if self.head is None:
return
elif self.head.next is None:
self.head = None
else:
# find the node before the last node
cur = self.head
while cur.next.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = None
# print out the list
def display(self):
cur = self.head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.data, end="->")
cur = cur.next
print()
# create a linked list
my_list = LinkedList.LinkedList()
# insert some node
my_list.insert(5)
my_list.insert(1)
my_list.insert(8)
my_list.insert(3)
my_list.insert(7)
# print all the nodes in the list
my_list.display()
# delete a node
my_list.delete()
my_list.display()
# delete a node
my_list.delete()
my_list.display()
# insert a node
my_list.insert(6)
my_list.display()Output:
5->1->8->3->7->
5->1->8->3->
5->1->8->
5->1->8->6->Stack and queue
Stack and queue are important data structures in computer science, which can be used in many situations for efficiency. Stacks are a Last In First Out (LIFO) data structure. Queues are a First In First Out (FIFO) data structure.
Stacks and queues are used directly or indirectly in various different programming situations. For instance, Python codes are normally executed in the order they appear, in queue ordering in other words. Meanwhile, recursive function calls (and function calls in general) are handle through the call stack, meaning the first recursive function call is the last to be resolved.
Stacks and queue can be implemented using linked list. But in these case, we no long have access to the node in the middle of the list. Instead, we can only add or delete from the front or the end. More details will be shown in the data structures.
Reference:
GreeksforGreeks – Python Linked List: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-linked-list/
